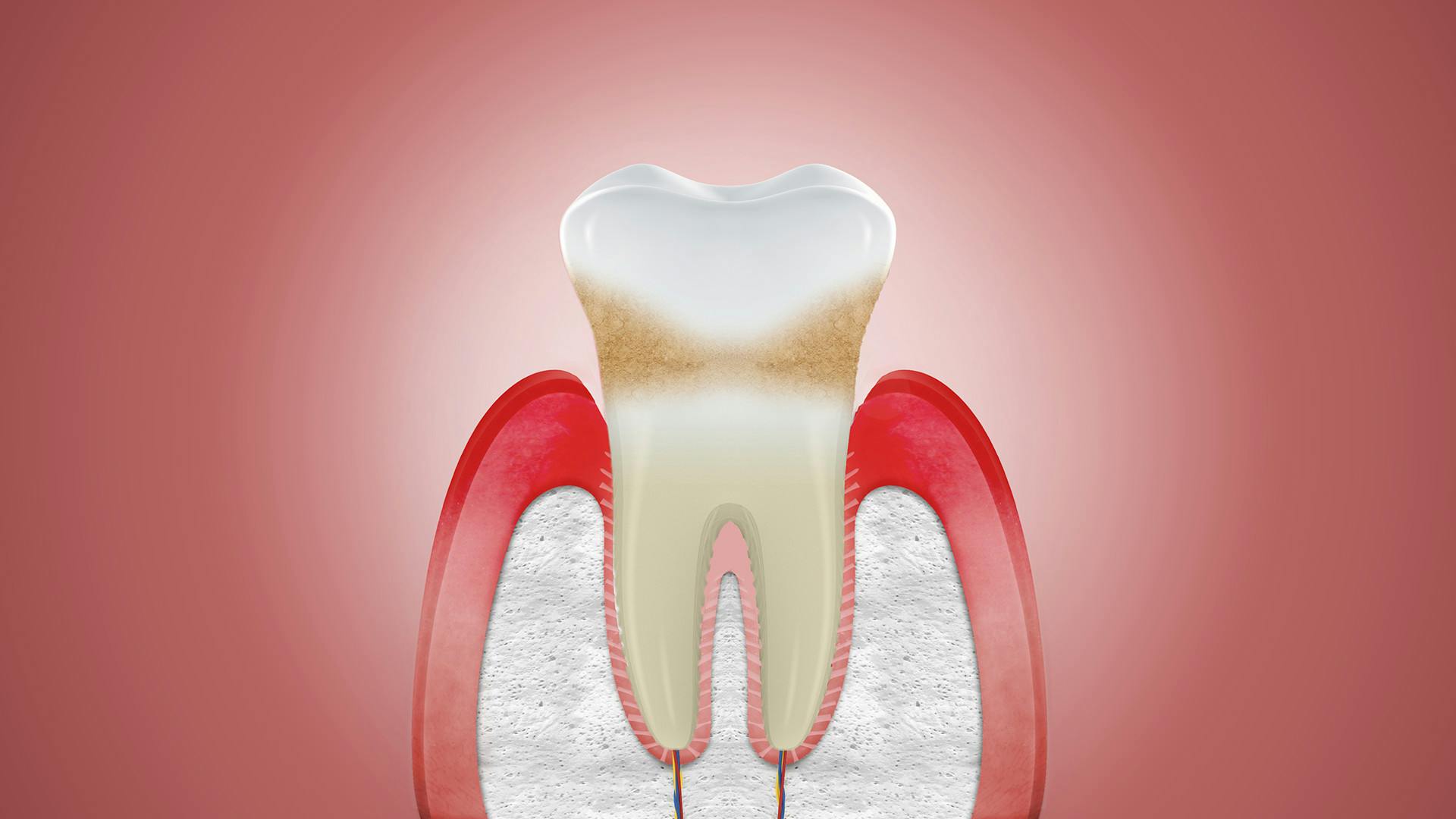
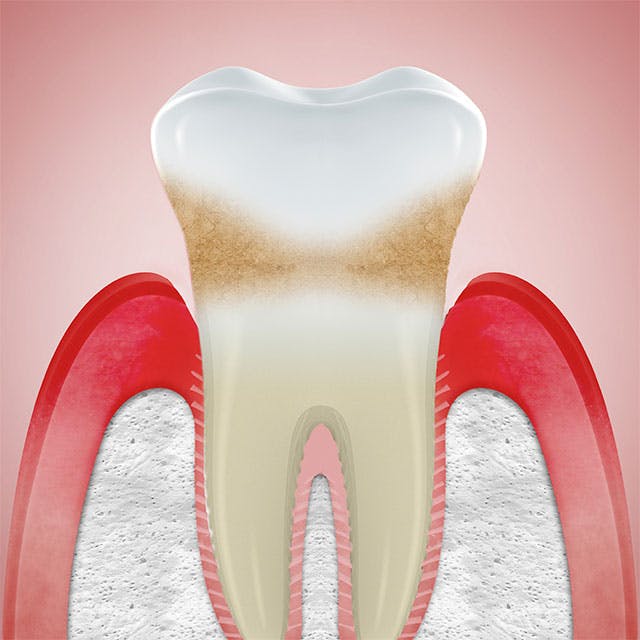
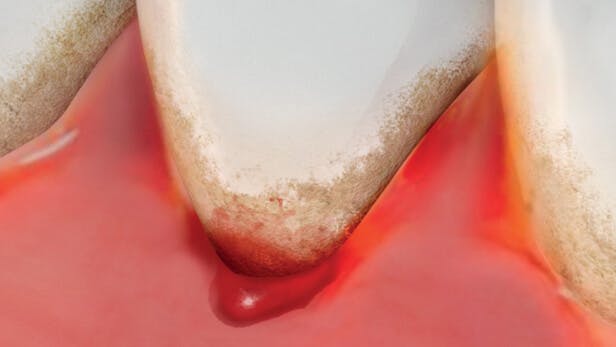
CAN RECEDING GUMS GROW BACK?
The simple answer is, no. If your gums are damaged by, for example periodontitis, the most severe form of gum disease, it’s not possible for receding gums to grow back.1 However, even though receding gums can’t be reversed there are treatments that can help to stop the problem from getting worse.
HOW CAN I TELL IF I HAVE RECEDING GUMS?
There are a few signs you might spot that can tell you if you have gum problems, or gum recession. It happens when your gums pull back from your teeth, leaving the root beneath exposed and the first thing you might feel is increased tooth sensitivity. You might also notice that your teeth look longer, or feel a notch where the gum meets the tooth.2
While you may see these signs, it’s not always easy to tell if you have receding gums. The best thing to do is have regular check ups with your dentist, as a professional can identify and treat gum problems. This is particularly important with receding gums as getting treatment as soon as possible is the best way to stop them from getting worse.
WHAT CAUSES RECEDING GUMS?
There are many factors that can cause your gums to recede and your dentist will be able to tell you which is causing your gum recession:3
- Brushing your teeth too hard – this can wear away the enamel on your teeth and make your gums recede.4
- Poor oral health – if you don’t keep your teeth clean with regular brushing and flossing, plaque can build up and turn into a hard deposit called tartar. If this isn’t removed it can lead to gum disease and gum recession.
- Grinding or clenching your teeth – if this is severe it can put pressure on your gums which can cause them to recede.
- Smoking – if you smoke you are more likely to get receding gums.5
- Periodontitis – In severe gum disease, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the teeth and form pockets. These may become infected and when they do this can damage the tissue and bone that holds teeth in place making them loose and wobbly. It can even lead to tooth loss.6
HOW CAN I STOP RECEDING GUMS?
If you want to find out if you have gum recession or think you have receding gums, the first thing to do is book an appointment to see your dentist and get professional advice on how to stop receding gums.
There are several receding gum treatments including:
Scaling and root planing
In cases of gum recession, your dentist might suggest scaling and root planing. This is a two-part procedure done by your dentist. Firstly, all the plaque and hardened tartar above and below the gum line (where the gum meets the tooth) is removed. Then your dentist will do root planing, which is smoothing out your teeth roots to help the gums reattach to the teeth. Your dentist may offer a local anesthetic during the procedure and it may take more than one visit to complete.
After your treatment it’s normal for your gums to be red, swollen and sore and for there to be increased sensitivity.
Scaling and planing is often enough to fix the problem, 7 but you will need to have regular check ups to make sure your receding gums have improved and are not getting worse. It’s also important to maintain a good oral health routine to protect your gums.
Gum surgery
For more severe cases of receding gums your dentist may recommend gum surgery. There are few different types including:
- Open flap scaling and planing: If non-surgical treatment hasn’t worked, your dentist may recommend open flap scaling and planing, where the affected gum tissue is folded back to get better access to clean and smooth the roots. The gum is then reattached snugly, making it easier to keep clean and healthy.8,9
- Regeneration: This is surgical treatment that can help to regenerate the damaged bone and gum tissue. Your dentist will clean above and below the gum to remove bacteria and plaque. Then a regenerative material – a membrane, tissue-stimulating protein or graft tissue, will be applied to encourage your body to naturally restore the damaged bone and tissue. The gum is then securely reattached over the root of the tooth.10,11
Gum grafts
If gum tissue has been lost your dentist may suggest soft tissue, or gum graft, surgery. This is where tissue is grafted from surrounding gums or the roof of your mouth and stitched to the gum tissue to cover the exposed root of your tooth.12
HOW CAN I HELP TO PREVENT RECEDING GUMS
The best protection against receding gums is regular check ups with a dentist and a good oral health routine. Brushing twice daily with a fluoride toothpaste or a daily gum health toothpaste like parodontax, helps to remove plaque bacteria to keep your gums, and teeth, healthy.
1 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. 2017. Gingivitis and periodontitis: Overview. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0072777/?_ga=2.138519283.1783860827.1500461985-760127960.1500461985. [Accessed 19 July 2017]., 2 WebMD. 2017. Receding Gums: Causes, Treatment, Surgery, and Prevention. [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/receding_gums_causes-treatments#1. [Accessed 19 July 2017]., 3 WebMD. 2017. Receding Gums: Causes, Treatment, Surgery, and Prevention. [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/receding_gums_causes-treatments#1. [Accessed 19 July 2017]., 4 WebMD. 2017. Receding Gums: Causes, Treatment, Surgery, and Prevention. [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/receding_gums_causes-treatments#1. [Accessed 25 July 2017]., 5 British Society of Periodontology. 2016. The Good Practitioner’s Guide to Periodontology. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.bsperio.org.uk/publications/good_practitioners_guide_2016.pdf?v=3. [Accessed 19 July 2017]., 6 Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments . 2017. Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments . [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/OralHealth/Topics/GumDiseases/PeriodontalGumDisease.htm. [Accessed 19 July 2017]., 7 British Society of Periodontology. 2016. The Good Practitioner’s Guide to Periodontology. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.bsperio.org.uk/publications/good_practitioners_guide_2016.pdf?v=3. [Accessed 19 July 2017]., 8 British Society of Periodontology. 2016. The Good Practitioner’s Guide to Periodontology. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.bsperio.org.uk/publications/good_practitioners_guide_2016.pdf?v=3. [Accessed 19 July 2017]., 9 WebMD. 2017. Receding Gums: Causes, Treatment, Surgery, and Prevention. [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/receding_gums_causes-treatments#2. [Accessed 19 July 2017]., 10 British Society of Periodontology. 2016. The Good Practitioner’s Guide to Periodontology. [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.bsperio.org.uk/publications/good_practitioners_guide_2016.pdf?v=3. [Accessed 19 July 2017]., 11 WebMD. 2017. Receding Gums: Causes, Treatment, Surgery, and Prevention. [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/guide/receding_gums_causes-treatments#2. [Accessed 19 July 2017]., 12 Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments . 2017. Periodontal (Gum) Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments . [ONLINE] Available at: https://www.nidcr.nih.gov/OralHealth/Topics/GumDiseases/PeriodontalGumDisease.htm. [Accessed 19 July 2017].